Did You Know Facts About Glucose
What is glucose?
Glucose is too known as blood sugar. After eating carbs, your body breaks them downward into a type of elementary sugar called glucose that is then either stored or used for energy—and that's just the tip of the iceberg. Here's everything you demand to know about glucose, even if you don't accept diabetes.
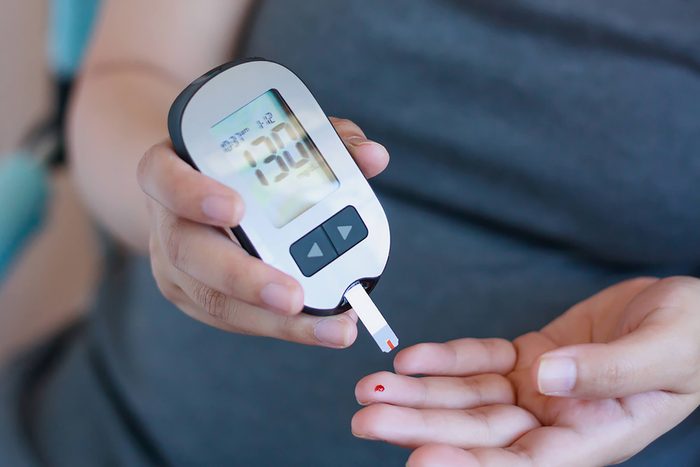
Claret sugar should be relatively low and steady
High blood glucose can be toxic and is a sign of prediabetes, so information technology's crucial to keep information technology in cheque. Co-ordinate to the Centers for Disease Command and Prevention (CDC), more than i out of iii Americans take prediabetes, and many don't know information technology because information technology causes few symptoms (or none at all). Then what is prediabetes? Typically when y'all eat nutrient, blood carbohydrate starts to rising so your body starts to produce the hormone insulin. Insulin normally lowers claret sugar levels because information technology signals the body cells to absorb the glucose and utilize information technology as fuel.
However, with prediabetes (which tin somewhen progress to type 2 diabetes), the body tin can ignore the effects of insulin, which is known as insulin resistance. That ways that even though at that place's insulin in the bloodstream, blood carbohydrate levels remain as well loftier, which can increase the risk of center disease, stroke, and other health problems. (Here'due south more on keeping your prediabetes from turning into Type 2.)
That'southward why anybody can benefit from learning most blood glucose and how to avoid having levels that are too high. You tin can take steps (like exercise) that aid reduce the gamble of insulin resistance (and follow these tips on maintaining stable blood carbohydrate levels).
So what should your claret glucose level exist? The American Diabetes Association says that a fasting glucose level of less than 100 mg/dl is normal, with 100 to 125 as prediabetes, and over 126 equally diabetes. (A fasting glucose examination is a blood test conducted subsequently you oasis't had any food or drink, except water, for eight hours.) Your hemoglobin A1C level—which is a blood test that detects levels in the previous ii to 3 months—should exist less than 5.seven pct.
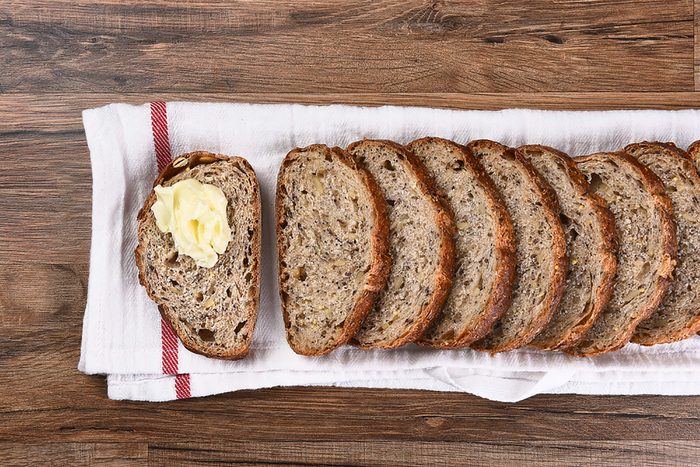

Food is turned into glucose
It tin be helpful to empathise what exactly glucose is. "When y'all eat food, your body needs to catechumen it into the simplest grade of free energy, which is glucose, to utilise information technology," says Erin Palinski-Wade, RD, certified diabetes educator (CDE), and writer of 2-Day Diabetes Nutrition. "Carbohydrates are the easiest food to convert into glucose, which is why they take the greatest impact on blood glucose levels." When nosotros eat carbs, they're broken downward into glucose as they're digested. Then, "glucose is absorbed by the cells lining the small intestine, into the bloodstream and delivered throughout the body," explains Tanya Zuckerbrot, MS, RD, a New York Urban center-based registered dietitian, bestselling author, and founder of The F-Cistron Diet.

Simple carbs can make glucose spike
In full general, carbohydrates are some of the healthiest foods you tin can eat, including legumes, fruit, and whole grains, only information technology's all-time to go easy on the "simple" or refined carbs like sugar-sweetened beverages, white staff of life, pasta, cakes, and other sweets. "The amount of carbohydrate consumed at one time and the type of saccharide—complex or simple—will take a great impact on glucose levels," Palinski-Wade says. (Here'south how to reverse the effects of a sugar binge.)
Zuckerbrot says to retrieve portion sizes when eating carbs. "One-third loving cup of rice, one-half a cup of pasta, and half a loving cup of lentils all equal 15g of carbohydrates or 1 serving of carbohydrates," she says. "Keep that in mind when portioning out your luncheon or dinner. Most restaurants give you double or triple the amount you should be eating in one sitting."
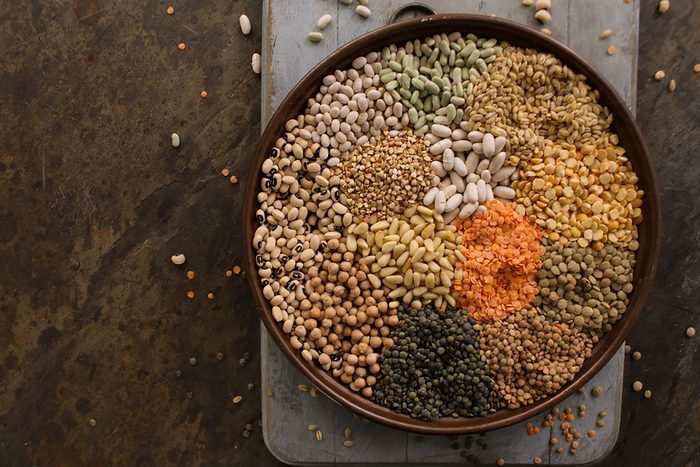

Cobweb helps keep claret sugar steady
Fiber is what makes complex carbohydrates complex—it's the zero-calorie, non-digestible role of a carbohydrate that adds bulk to nutrient and swells in the tummy when eaten. Studies have shown eating a diet rich in fiber can aid control claret carbohydrate. "Choosing high cobweb, complex carbohydrates volition slow downwardly how quickly nutrient is converted into glucose, which will help to stabilize glucose levels," Palinski-Wade says. Whole grains, fruits, nuts, legumes, and other vegetables are high in fiber. In addition, check where the foods you eat fall on the glycemic index and its glycemic load, which rate how chop-chop the food produces glucose every bit well as how many carbs it contains.
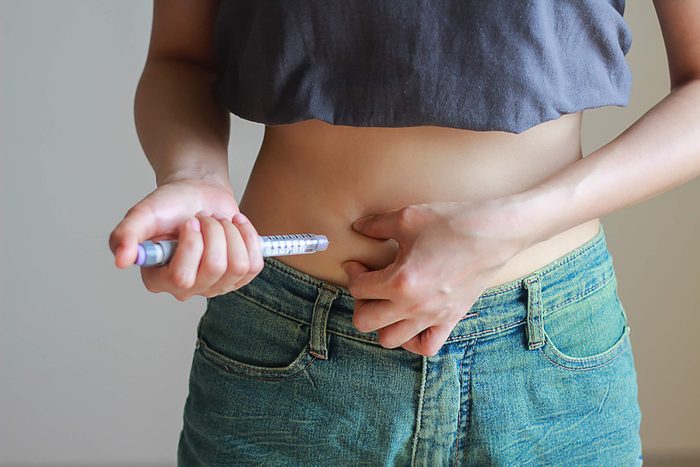

Insulin resistance tin cause claret sugar to be too high
"Blood glucose levels are controlled by two pancreatic hormones: insulin and glucagon," Zuckerbrot says. The pancreas makes insulin to help the torso blot glucose (nosotros'll get to glucagon later). "The pancreas secretes insulin at depression levels in between meals and while we sleep," says Idie Clement, RN, certified diabetes educator (CDE) of Piedmont Atlanta's Diabetes Resource Center. "When we eat, insulin is secreted quickly and takes the carbohydrate from the blood stream so it can create energy and keep the blood sugars in normal range."
Basically, insulin helps the torso blot glucose. But with prediabetes and blazon 2 diabetes, the body's insulin resistance leads to a buildup of glucose in the blood. People with blazon 2 diabetes tin gainsay insulin resistance and control their blood sugar with a combination of diet, practise, oral medication, and sometimes injecting additional insulin. People with type 1 diabetes, still, always need to accept insulin to survive because information technology's an autoimmune status that destroys the insulin-producing cells in the body. (Here are the differences betwixt type 1 and type 2 diabetes.)
Glucose fuels the brain
Although glucose then far sounds like a bad thing, you wouldn't exist able to survive without information technology. In fact, 1 of the amazing facts virtually your brain is that your noggin runs on glucose. Co-ordinate to Harvard University's Neuroscience Institute, the brain uses the nearly free energy out of all the body'south organs, and and then requires half of the torso's saccharide. In addition, "glucose is the chief source of free energy used past our bodies," Zuckerbrot says. Once your body has used the energy it needs, "glucose is stored as glycogen in the liver and muscles," she says. If your body runs depression on glucose, the pancreas will release its other hormone, glucagon. "Glucagon induces the liver to release stored glucose into the bloodstream," Zuckerbrot says.

Non eating is not skillful for glucose
Yous might ask, will skipping breakfast help lower claret sugar? It turns out that not eating is non an effective strategy for keeping glucose in bank check. "Spacing carbohydrate intake throughout the day to prevent consuming excessive amounts at in one case is the best fashion to ensure steady blood glucose levels," Palinski-Wade says. A stable blood sugar level means non having spikes or huge drops—plus, low levels might brand you overeat or eat unhealthily. "Low blood glucose levels tin can make it harder to concentrate, brand you cranky, and lead to excess snacking or cravings," Zuckerbrot says. "Keeping your blood sugar stable throughout the solar day can aid you avert side effects of low blood saccharide. Avoid skipping meals, and swallow every four to five hours."

Super-low blood sugar is dangerous
Every person who has diabetes should know these tricks to care for low claret carbohydrate—but what about everyone else? Turns out that although it's more than common in people who are taking insulin to treat diabetes, anyone can become hypoglycemic, which ways having dangerously low blood sugar levels. If an otherwise-healthy person develops system, it is likely because they have prediabetes and should encounter their doctor.
"Symptoms of hypoglycemia include feeling shaky, breaking out into a sweat, feeling your heart rate race or face up flush, hunger, and sometimes, if depression plenty get unconscious," says Clement. The treatment is to get some carbohydrate in you, fast—people with diabetes might carry glucose tablets, just if those aren't available drink a cup of juice, Cloudless says.

Super-high claret sugar is also unsafe
The other blood sugar extreme is high blood saccharide, or hyperglycemia. "Hyperglycemia happens when excessive amounts of glucose are in the bloodstream, typically as a effect of [a person with diabetes] consuming too many carbohydrates, which convert into glucose in the blood," Palinski-Wade says. "This can lead to fatigue, excess thirst, and excessive urination. If claret glucose levels climb to extremely loftier levels, the risk of loss of consciousness, coma, and even expiry are possible." This is another reason that people with diabetes demand to consume the right portions of carbs throughout the entire day, or have enough insulin to process the nutrient they are eating. (Here's more on the difference betwixt hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia.)
A complex mix of factors tin touch claret sugar in people with diabetes. Stress or an infection tin make it harder for medication to command claret sugar; exercise can lower blood saccharide (in a good way), and consuming carbs with fat, protein, or cobweb can also slow downwardly digestion of carbohydrates and reduce the claret sugar touch on the body.
It'south rare for at that place to be symptoms of very high blood carbohydrate in people without diabetes. In those cases, it might exist triggered by serious illnesses, some medications, stomach surgery, or low levels of sure hormones, reports the Hormone Wellness Network.
Type 1 and blazon 2 diabetes are very different weather
Learning about the unlike types of diabetes—there are several means glucose can be mismanaged by the torso—can be an important preventive strategy. Type two diabetes, in which your torso develops insulin resistance, is the virtually common type of diabetes and often develops later in life (although children can become it too). Genetics and lifestyle play a role in blazon 2 diabetes, which can sometimes exist delayed or prevented by sticking to a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, and fugitive weight proceeds. Type one diabetes, all the same, can not exist prevented with lifestyle choices. Type 1 diabetes occurs when the pancreas stops making insulin due to an autoimmune attack; it can exist diagnosed in children and young adults and is sometimes called "juvenile diabetes." (These surprising habits can lead to type two diabetes.)

Illness or stress tin affect your glucose level
1 manner stress could exist making you sick is by increasing the run a risk that blood sugar will ascension. "Stress and illness causes high blood glucose levels because during these times, your liver releases extra glucose to ensure enough energy is readily bachelor," Zuckerbrot says. "At the same time, cortisol and growth hormone are released which makes your torso less sensitive to insulin. As a result, blood glucose levels are higher than usual." But it'south non irreversible: Research inDiabetology & Metabolic Syndrome found that people with diabetes were able to reduce their glucose levels after stress management preparation with a psychologist where patients learned muscle relaxation techniques, among others.

Inactivity also negatively affects blood sugar
As if you lot needed more science-backed reasons to exercise, hither's another: You can help regulate your glucose levels and reduce your risk of prediabetes and type 2 diabetes with exercise. Why is inactivity linked to higher blood saccharide? "Inactivity leads to a decrease in your insulin sensitivity and increases your insulin requirements," says Zuckerbrot. Practice uses up your trunk's glucose, making you lot more sensitive to insulin. According to the American Diabetes Association, physical activity can lower your blood glucose for upward to 24 hours or more than after you work out, and regular practice can lower your overall claret glucose level (A1C). On the other hand, research published in theJournals of Gerontology found that ii weeks of inactivity could increase the risk of blood sugar-control issues in older, overweight people who already had prediabetes.

HIIT grooming, specifically, could assistance glucose
High-intensity interval preparation (HIIT) is one of the all-time anti-aging workouts and one of the ways it may increase your longevity is by lowering glucose levels. "Researchers at the University of Turku, Finland, studied how high-intensity interval training alters the encephalon'south glucose metabolism in physically inactive insulin-resistant people," Zuckerbrot says. "Simply two weeks of HIIT preparation reduced glucose metabolism in all areas of the brain." An before study by the aforementioned researchers found that HIIT increased glucose metabolism in muscles also. Because the encephalon runs on glucose, this conditioning could benefit your mind besides as your body.

Belly fatty is particularly bad for claret sugar
Research has found that having excess fat on the body can affect the take chances of diseases like type 2 diabetes, and where it's located on the body can affair likewise. Visceral fat—the type of fat that pads organs in the belly—puts you at a higher take chances of blazon two diabetes, according to a 2018 study inNature Genetics. Belly fat (which tin exist either visceral or subcutaneous fat, or fat underneath the pare) is known to promote inflammation and increase the gamble of insulin resistance. And another study from Massachusetts General Hospital found that it'southward non just an clan—there are actually genetic variants associated with an apple tree shape-body (carrying weight around the midsection rather than the arms or legs) that predisposes a person to type 2 diabetes. Merely the adept news is, co-ordinate to the American Diabetes Association, that even losing 10 to 15 pounds tin can make a big difference in your power to control claret sugar.

Blood sugar tests are important
So, should you get your claret sugar levels checked? It will likely depend on your age and risk factors. The American Diabetes Association suggests asymptomatic people get tested at a minimum every 3 years over age 45. Only, because high blood sugar is "often asymptomatic and can cause complications if left untreated, people with risk factors such as being overweight, having a high-take chances race or ethnicity [such as African-American], or lipid problems should exist screened periodically with a blood examination," says endocrinologist Kathleen Dungan, MD, of The Ohio Land Academy Wexner Medical Centre. In addition, "anyone with a family history of diabetes should get their glucose tested and inquire virtually having your A1C checked every bit part of their annual visit to their primary care physician," Cloudless says. If you have hazard factors, talk to you doctor about how often you should be screened and what age to start.
If you lot're meaning, a physician will as well have you take a glucose tolerance exam, which involves drinking a sugary liquid to see how your body responds. It's a test that tin can pick up gestational diabetes. "During pregnancy, women's bodies accept to produce three times more insulin than normal," Clement says. "Not everyone can handle this increased demand, and for those women, blood sugar starts going up around the 23rd or 24th week of pregnancy. These women probable will be placed on a special diet to control blood saccharide."

Yous should tell your doctor nearly these symptoms
If you have any of the signs of high blood sugar, you should definitely let your doctor know. If you're constantly thirsty, have frequent urination, and are extremely tired, that could point to a blood saccharide event. You should bring your concerns to your doctor especially if you have boosted risk factors like existence overweight, not exercising, and having a family unit history of diabetes. But because more 84 percent of people with prediabetes don't know they take it according to the CDC, the best strategy is to have steps to prevent the status and get tested, particularly if y'all are at higher hazard of type two diabetes.

Cinnamon may improve your glucose level
Besides flavoring food, cinnamon might have potential health benefits. "Some inquiry indicates cinnamon may improve insulin sensitivity," Palinski-Wade says. "For those with insulin resistance, this may assistance the body to process glucose more than easily, resulting in less of a rise in blood glucose levels."

Nutrient order may touch on glucose levels
Among the sneaky things that raise your blood sugar levels may be the order in which you eat foods during any given repast. Inquiry from Weill Cornell Medical College tested what happened when participants ate the same meal on different days. Offset they ate carbs, followed by protein, vegetables, and fat; some other solar day they ate the protein, veggies, and fat first, followed by the carbs. Both glucose and insulin were lower when they ate the carbs last. Palinski-Wade says eating the carbs later the other foods may slightly reduce the fourth dimension it takes to convert the carbs into glucose, preventing a fasten after a repast.

Glucose levels may be linked to dementia and Alzheimer'due south
There may exist more kinds of diabetes than nosotros know, such every bit type 3c, which occurs later on pancreatitis. But there's withal some other type that researchers have been exploring. "Researchers are looking at how sugar affects the brain—specifically, some are referring to Alzheimer'due south illness as type three diabetes because of this inquiry," Clement says. This isn't exactly surprising given the brain's reliance on glucose for proper operation. In addition, diabetes tin can damage blood vessels, which tin prevent your brain from getting the blood flow it needs. One study of over 2,000 participants found that glucose levels in those who went on to develop dementia were elevated—even among people without diabetes. The findings suggest high blood saccharide could be a take chances factor for dementia.

Mindfulness may reduce glucose levels
Mindfulness may help your claret sugar level. In a 2016 written report from Brown University, participants with high scores for mindfulness, which they defined as existence enlightened of your present thoughts and feelings, were more likely to have healthy glucose levels than people with low scores. The researchers surmised that although it's only an association, not a crusade and issue, mindful people were more likely to self-motivate themselves to exercise and eat right, and to resist cravings. According to report writer Eric Loucks, this was the first written report to look at the connectedness betwixt diabetes and mindfulness, which may be a new way to reduce your chance. Effort starting your morn with these mindfulness exercises.

Artificial sweeteners don't do good blood sugar—or do they?
At that place's mixed reviews about the touch of artificial sweeteners on blood carbohydrate level. Some research has suggested that the sweet taste is enough to fox your torso'south response, as if it was actually receiving sugar. But, the sweetener stevia may concord some promise for really reducing blood sugar, according to one study. "Some research suggests stevia may have a beneficial impact on blood glucose levels, still, more research needs to be done in this area," Palinski-Wade says.

Poor sleep isn't great for blood carbohydrate
Fact: You are more likely to eat more when you're slumber deprived. Plus, yous'll likely exist craving junk food, which is non exactly great for your blood sugar level. According to the National Sleep Foundation, the connexion may be considering with lack of sleep, hormones go out of whack, and the stress hormone cortisol may prevent insulin from doing its job properly. With short-term sleep deprivation, levels can get back to normal with two nights of skilful sleep. But for long-term issues sleeping, including slumber apnea, run across your doc to reduce your diabetes take chances.

There are several ways to self-test blood sugar
One of the well-nigh important tests people with diabetes apply is the daily finger prick, in which a drop of blood is placed on a test strip and inserted into a blood saccharide meter to quickly get a blood sugar reading. People with diabetes often need to self-test their claret sugar (especially if they are on insulin) to make sure it'due south steady. However, there are other ways to self-exam blood carbohydrate, including continuous glucose monitors. More often used past people with type 1 diabetes, the devices use a small sensor wire that is inserted below the skin's surface to continuously monitor glucose levels. The sensors demand to be replaced every 3 to vii days, and people who use them typically still demand to do finger-prick tests to make sure the devices are working correctly.

Become educated virtually diabetes management
At that place are scientific discipline-backed strategies to drop blood saccharide dorsum to a normal range, and Cloudless says she puts diabetes education at the forefront of what everyone should know near glucose. "There is not plenty emphasis on the consequences of uncontrolled diabetes and resulting complications such as neuropathy, heart affliction, centre disease, and kidney affliction," she says. "In addition to good medical care, diabetes self-management education can help patients acquire to have care of their disease."
Sources
- American Diabetes Association: "Diagnosis"
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: "The A1C Test & Diabetes"
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: "Prediabetes: Your Chance to Prevent Type two Diabetes"
- Erin Palinski-Wade, RD, Certified Diabetes Educator (CDE), and author of 2-Day Diabetes Nutrition
- Tanya Zuckerbrot, MS, RD, a New York City-based registered dietitian, bestselling author, and founder of The F-Factor Diet.
- Bioactive Carbohydrates and Dietary Fibre: " Dietary fibre for glycaemia control: Towards a mechanistic understanding"
- Harvard Medical School: "Glycemic index for 60+ foods"
- Idie Clement, RN, Certified Diabetes Educator (CDE) of Piedmont Atlanta's Diabetes Resource Heart
- Harvard Medical School: "Carbohydrate and the Encephalon"
- U.South. National Library of Medicine: "Diabetes Type 1"
- Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome: "The efectiveness of stress management grooming on claret glucose control in patients with type 2 diabetes"
- American Diabetes Association: "Blood Sugar and Practise"
- The Journals of Gerontology: "Failed Recovery of Glycemic Control and Myofibrillar Protein Synthesis With 2 wk of Physical Inactivity in Overweight, Prediabetic Older Adults"
- Scandinavian Journal of Medicine & Science in Sports: "Increased insulin‐stimulated glucose uptake in both leg and arm muscles after sprint interval and moderate‐intensity training in subjects with type 2 diabetes or prediabetes"
- Journal of Cerebral Blood Menstruum & Metabolism: "Brusk-term interval grooming alters brain glucose metabolism in subjects with insulin resistance"
- Nature Genetics: "Regulatory variants at KLF14 influence type 2 diabetes take chances via a female-specific upshot on adipocyte size and trunk composition"
- JAMA: "Genetic Association of Waist-to-Hip Ratio With Cardiometabolic Traits, Type 2 Diabetes, and Coronary Heart Affliction"
- American Diabetes Association: "Extra Weight, Extra Risk"
- American Diabetes Association: "two. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes"
- Centers for Illness Command and Prevention: "The Surprising Truth About Prediabetes"
- Clinical Diet: "Efficacy of cinnamon in patients with type II diabetes mellitus: A randomized controlled clinical trial"
- American Diabetes Association: "Food Society Has a Pregnant Impact on Postprandial Glucose and Insulin Levels"
- Weill Cornell Medical Center: "Nutrient Order Has Significant Impact on Glucose and Insulin Levels"
- The New England Journal of Medicine: "Glucose Levels and Risk of Dementia"
- American Journal of Health Behavior: "Associations of Mindfulness with Glucose Regulation and Diabetes"
- Current Biological science: "Integration of Sweet Taste and Metabolism Determines Carbohydrate Advantage"
- Medscape: "Bogus Sweeteners Alter Gut Response to Glucose"
- Nature Communications: "Steviol glycosides enhance pancreatic beta-cell function and gustation sensation past potentiation of TRPM5 channel activity"
- National Slumber Foundation: "The Link Betwixt a Lack of Slumber and Type 2 Diabetes"
- American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Intendance Medicine: "Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Incident Diabetes. A Historical Accomplice Written report"
- European Periodical of Clinical Nutrition : "The effects of partial slumber deprivation on energy residual: a systematic review and meta-analysis"
- Nutrition and Metabolism: "Effects of resveratrol on glucose control and insulin sensitivity in subjects with type 2 diabetes: systematic review and meta-analysis"
- U.South. Food and Drug Administration: "FDA approves get-go continuous glucose monitoring system for adults non requiring blood sample scale"
- Hormone Health Network : "Non Diabetic Hypoglycemia"
![]() Medically reviewed past
Medically reviewed past
Originally Published: Nov 21, 2017
Source: https://www.thehealthy.com/diabetes/type-2-diabetes/glucose-facts/
0 Response to "Did You Know Facts About Glucose"
Post a Comment